-
 Trenching and Excavations are among the most hazardous construction operations. Cave-ins pose the greatest risk and are more likely than some other excavation-related incidents to result in worker fatalities. When done safely, trenching operations can reduce worker exposure to cave-ins, falling loads, hazardous atmospheres, and hazards from mobile equipment. OSHA requirements include Competent Person, inspections, proper access, training, and much more.
Trenching and Excavations are among the most hazardous construction operations. Cave-ins pose the greatest risk and are more likely than some other excavation-related incidents to result in worker fatalities. When done safely, trenching operations can reduce worker exposure to cave-ins, falling loads, hazardous atmospheres, and hazards from mobile equipment. OSHA requirements include Competent Person, inspections, proper access, training, and much more. -
 Millions of workers in the construction industry work on scaffolds. Scaffold incidents causing injury or death to workers is often the result of either the planking or support giving way, by the worker slipping, the absence of fall protection, or being struck by a falling object. Preventing scaffold accidents include design by a qualified person, fall protection, proper guardrails, platform construction, safe access, inspections, training, and much more.
Millions of workers in the construction industry work on scaffolds. Scaffold incidents causing injury or death to workers is often the result of either the planking or support giving way, by the worker slipping, the absence of fall protection, or being struck by a falling object. Preventing scaffold accidents include design by a qualified person, fall protection, proper guardrails, platform construction, safe access, inspections, training, and much more. -
 Aerial Work Platforms (AWPs) are now called Mobile Elevating Work Platforms (MEWPs). Aerial lifts have replaced ladders and scaffolding on many job sites due to their mobility and flexibility, however many workers are injured or killed on them each year. An aerial lift is any vehicle-mounted device used to elevate personnel, most commonly include articulating (jointed) boom platforms and extendable boom platforms. Most frequent hazards are falls, electrocutions and tip-overs.
Aerial Work Platforms (AWPs) are now called Mobile Elevating Work Platforms (MEWPs). Aerial lifts have replaced ladders and scaffolding on many job sites due to their mobility and flexibility, however many workers are injured or killed on them each year. An aerial lift is any vehicle-mounted device used to elevate personnel, most commonly include articulating (jointed) boom platforms and extendable boom platforms. Most frequent hazards are falls, electrocutions and tip-overs. -
 Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms in human blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to, hepatitis B (HBV), hepatitis C (HCV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Key terms are Exposure Control Plans, Universal Precautions, Bloodborne Path Kits, Personal Protective Equipment Hepatitis B Vaccination, and Post-exposure follow-up.
Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms in human blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to, hepatitis B (HBV), hepatitis C (HCV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Key terms are Exposure Control Plans, Universal Precautions, Bloodborne Path Kits, Personal Protective Equipment Hepatitis B Vaccination, and Post-exposure follow-up. -
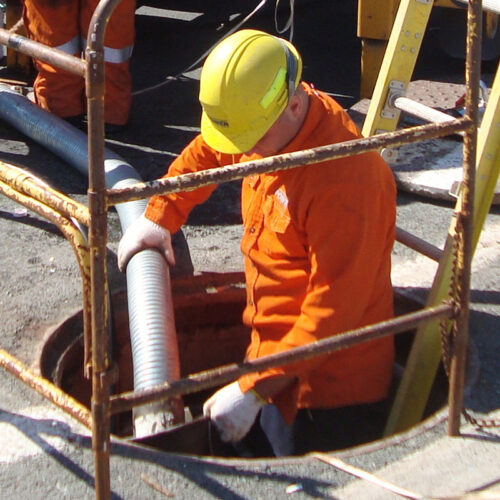 Confined spaces may be encountered in both General Industry and Construction and pose numerous physical and environmental hazards. Critical is the need for employers to understand the risks, the regulations, and implement training and hazard mitigation techniques. Employees must have proper training, equipment, and work procedures to safely enter.
Confined spaces may be encountered in both General Industry and Construction and pose numerous physical and environmental hazards. Critical is the need for employers to understand the risks, the regulations, and implement training and hazard mitigation techniques. Employees must have proper training, equipment, and work procedures to safely enter. -
 Electricity has long been recognized as a serious workplace hazard, exposing employees to electric shock, electrocution, burns, fires, and explosion. Electrical hazards cause more than 300 electrocutions and 4,000 injuries in the workplace each year. The construction industry leading with the highest electrical fatality rate.
Electricity has long been recognized as a serious workplace hazard, exposing employees to electric shock, electrocution, burns, fires, and explosion. Electrical hazards cause more than 300 electrocutions and 4,000 injuries in the workplace each year. The construction industry leading with the highest electrical fatality rate. -
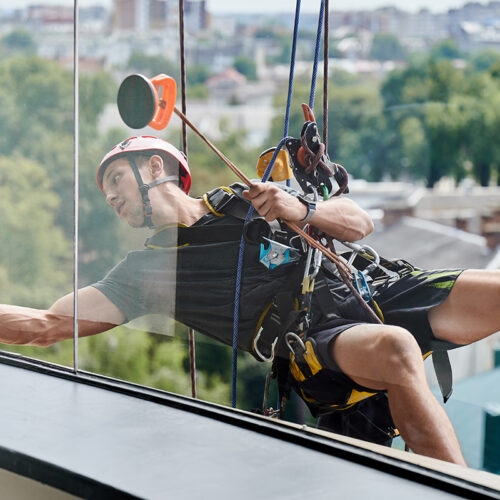 Falls are among the most common causes of serious work-related injuries and the leading cause of death in construction. Prevention is the key and it starts with planning to identify the hazards, providing the right fall protection equipment, and training workers on hazard recognition and mitigation.
Falls are among the most common causes of serious work-related injuries and the leading cause of death in construction. Prevention is the key and it starts with planning to identify the hazards, providing the right fall protection equipment, and training workers on hazard recognition and mitigation. -
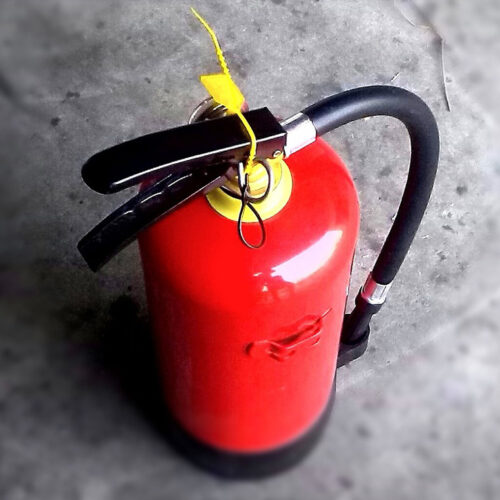 There are an average of 37,000 fires at industrial facilities every year (NFPA). These fires are catastrophic and cause serious and fatal injuries, and cost billions of dollars annually. The purpose of the fire prevention plan is to eliminate the causes of fire, prevent los of life and property and to comply with OSHA. OSHA strongly recommends that all employers have a fire prevention plan, but it is only required in a few regulations.
There are an average of 37,000 fires at industrial facilities every year (NFPA). These fires are catastrophic and cause serious and fatal injuries, and cost billions of dollars annually. The purpose of the fire prevention plan is to eliminate the causes of fire, prevent los of life and property and to comply with OSHA. OSHA strongly recommends that all employers have a fire prevention plan, but it is only required in a few regulations. -
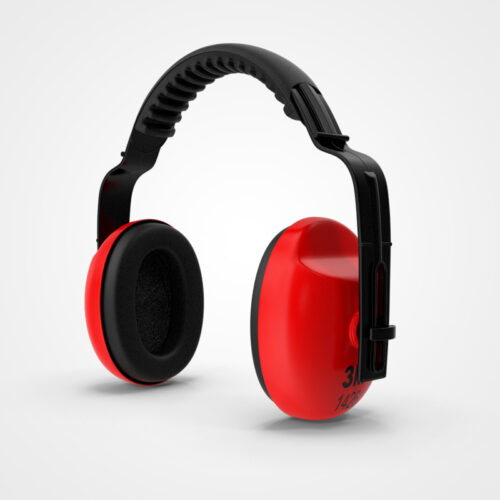 The Center for Disease Control (CDC) estimates that 22 million workers are exposed to potentially damaging noise at work each year. The result is permanent hearing loss that cannot be corrected through surgery or with medicine. Key terms are: Noise Monitoring, Written Hearing Conservation Program, Engineering Controls, PPE, and Employee Safety Training.
The Center for Disease Control (CDC) estimates that 22 million workers are exposed to potentially damaging noise at work each year. The result is permanent hearing loss that cannot be corrected through surgery or with medicine. Key terms are: Noise Monitoring, Written Hearing Conservation Program, Engineering Controls, PPE, and Employee Safety Training. -
 “Lockout/tagout”, aka The Control of Hazardous Energy, refers to specific practices and procedures to safeguard employees from the unexpected energization or startup of machinery and equipment, or the release of hazardous energy during service or maintenance activities. To help avoid accidents, injuries, and OSHA citations, look here to find all you need to implement an effective LOTO program.
“Lockout/tagout”, aka The Control of Hazardous Energy, refers to specific practices and procedures to safeguard employees from the unexpected energization or startup of machinery and equipment, or the release of hazardous energy during service or maintenance activities. To help avoid accidents, injuries, and OSHA citations, look here to find all you need to implement an effective LOTO program.


